|
|
Home
Pearsall Family DNA
Surname Project
Number of Pearsalls By Location
Maps by Family
Surname
The History of the Parshall Family from the Conquest of England by
William of Normandy, A.D. 1066 to the Close of the 19th Century
(1903)
The Parshall Family A.D. 870-1913 (1915)
History and Genealogy
of the Pearsall Family in England and America (1928)
Front Cover
Inside Front Cover
The Motive
Thanks
Illustrations
Contents
|
|
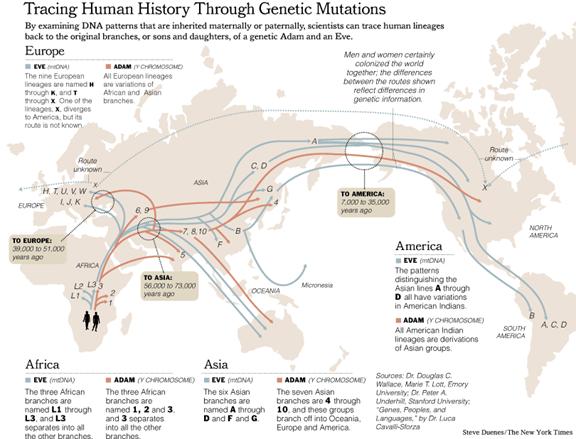
Migration – we keep moving…
Humans originated in Africa
many thousands of years ago based both on the fossil record as well as
genetic studies. About 55 – 75 thousand years ago, humans as we know today
(homo sapiens) ventured from Africa (around present-day Ethiopia), crossing the Red Sea between
present-day Djibouti
and Yemen.
From Yemen,
hunting/gathering bands rapidly moved along the coast of the Indian Ocean
traversing what are present-day Oman,
the Gulf (U.A.E., Qatar,
Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Iraq,
and Iran), Pakistan, India,
Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia,
and Indonesia, into Australia.
This migration around the Indian Ocean
was quite rapid, taking place over about 15 thousand years.
In the initial dispersal out of Africa, some groups stayed behind as others moved
forward. One fork in the migration path would have been through the rich
river basin of the Euphrates and Tigris
rivers. Over time, as human populations grew along the banks of the
Euphrates and the Tigris, some groups would venture further and further
up-stream into virgin lands of present-day Syria
and Turkey.
From there, some tribes went westward from Anatolia into the Balkans and
the rest of Europe, others went north through the Caucuses into eastern
Europe and the Urals, and others moved eastward into Central
Eurasia around the Caspian and Aral seas. This took place
between 25 to 40 thousand years ago.
Another African group also broke out of
Africa through Nile River into the Sinai Peninsula, then into the
Middle East and around the Mediterranean Sea.
This occurred about 30 thousand years ago; almost 50 thousand years after
the first group crossed the Red Sea.
Agriculture, or farming, began about
12,000 years ago. With the advent of domestication of crops and animals,
humans became “anchored” to the land. Climate variation such as drought
or disease had potentially disruptive impacts on settlement. During times
of significant change, populations would collapse, and rebuild or
resettle. The more successful civilizations that could accumulate and
manage agricultural wealth typically were situated in fertile areas such
as the Nile delta, between the Euphrates and Tigris, along the Indus River,
and parts of China.
In other climate/vegetation zones such as heavily wooded alpine, grassy
steppe, or tundra areas, people continue to migrate with the animals they
hunted.


Y-DNA (male) genetic migration and timeline:

Mitochondria-DNA (female) genetic
migration and timeline:

Timescales
We can derive
how groups are related based on haplotype STR
values and unique SNP (“snip”) marker results. Downstream populations
share the SNP values of upstream ancestors. Over time, mutations occur
new groups can be identified based on changes in SNP and haplotype marker results. Additionally, the more haplotype marker values groups or individuals have in
common, the more closely related. Timescales we can analyze are from many
thousands of years to several hundred years.
Haplogroups generally cover large populations. As an
example, Haplogroup I can be found in many
populations throughout Europe, from the Balkans, to Scandinavia, Sardinia and many other places. Haplogroup
I can be further broken down into “sub-clades”
(or sub-groups). Examples Haplogroup I sub-clades
include: I1a, I1b1, I1b2. Haplogroup I1a and I1b1 diverged about 1080
generations (or about 25,000 years ago). Haplogroup
I1b1 and I1b2 diverged about 270 generations (or about 7,000 years
ago). Within sub-clades with greater haplotype
marker resolution, we can find groups of families, and with even greater haplotype resolution, even sub-groups within families
can be identified.

Link to a general view of Haplogroup
I tree ŕ
Link to a more detailed view of Haplogroup I1b1* migration ŕ
Link to a more detailed view of Haplogroup I1a migration ŕ
Link to a more detailed view of Haplogroup E3b migration ŕ
Link to closely related Y-DNA families ŕ
###
|
|